2024 IRG-2: Machine learning-guided investigation of conductivity mechanisms in peptide assemblies
Certain peptides self-assemble fibers that exhibit long-range charge transport. Thermal fluctuations have been implicated as important in this emergent property.1
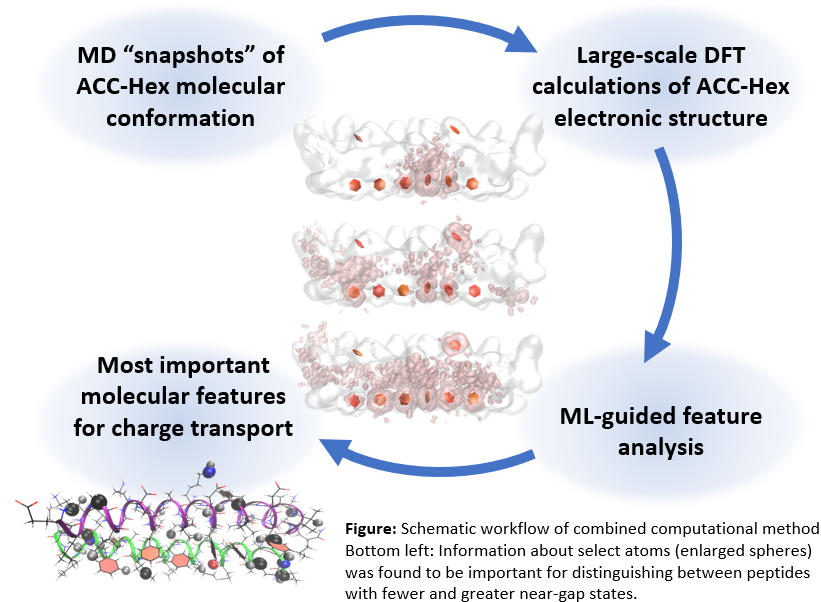
We adapted our interpretable machine learning (ML) platform2 to understand how thermal fluctuations in ACC-Hex peptide dimer nuclear structure influences electronic structure and therefore conductivity.
•Combined large-scale DFT calculations of 103 peptide dimer snapshots together with ML feature analysis.
•Extracted trends learned by ML classifier to determine which regions of the peptide are most relevant for the number of near-gap states.
•Used ML-guided feature analysis to determine the most important dimer molecular conformation parameters for controlling the number of near-gap states.
Our results show that both the arrangement of aromatic residues and the hydrogen bonding network of the peptide dimer are critical for describing electronic structure relevant for charge transport. These aspects will inform design efforts for peptides that assemble electronic materials.
1Lewis, et al. JPC C 2022.
2Mastracco, et al. ACS Nano 2022.
3 Mastracco, Mohanam, et al. In preparation.